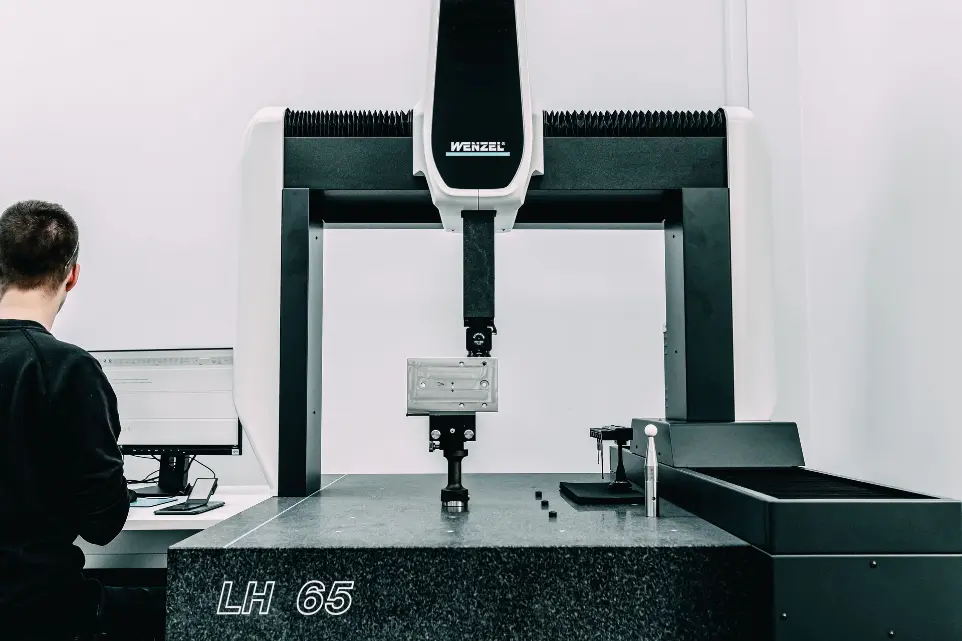
What is quality control and why is it crucial?
Quality control is a systematic process of monitoring and evaluating each stage of production to ensure that every manufactured part meets strict technical standards. This minimizes the risk of errors, reduces rework costs, and builds customer trust.
What quality control methods do we use?
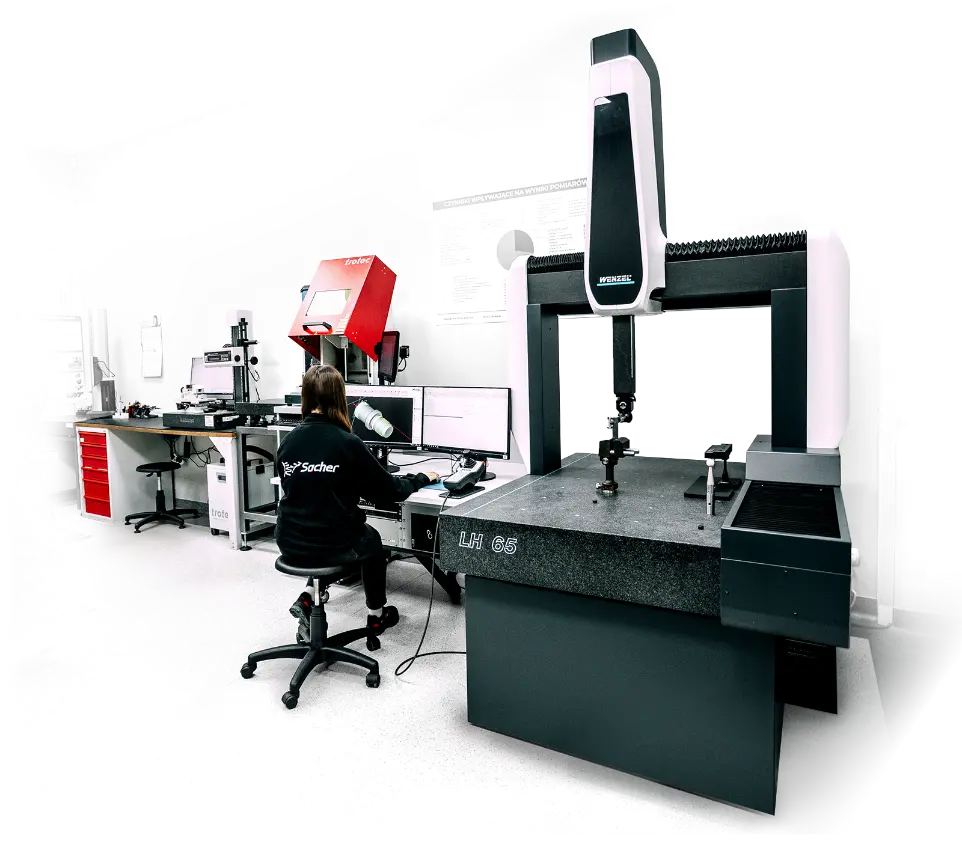
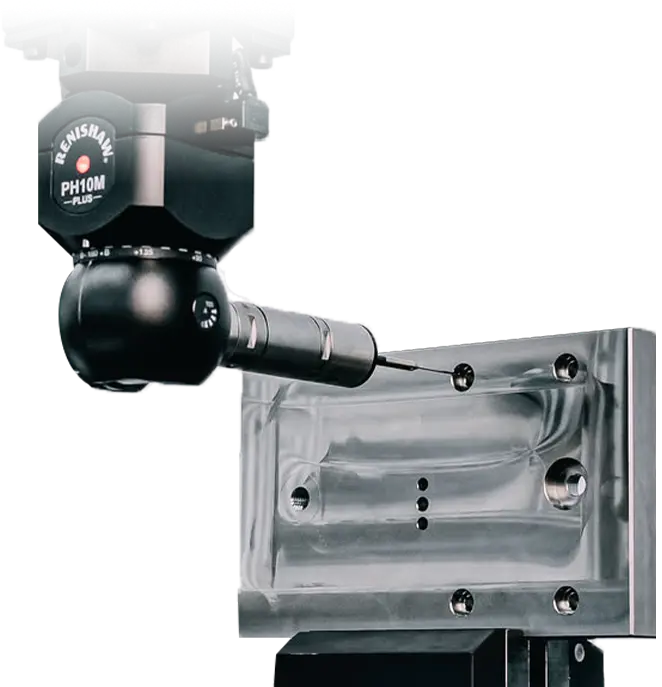
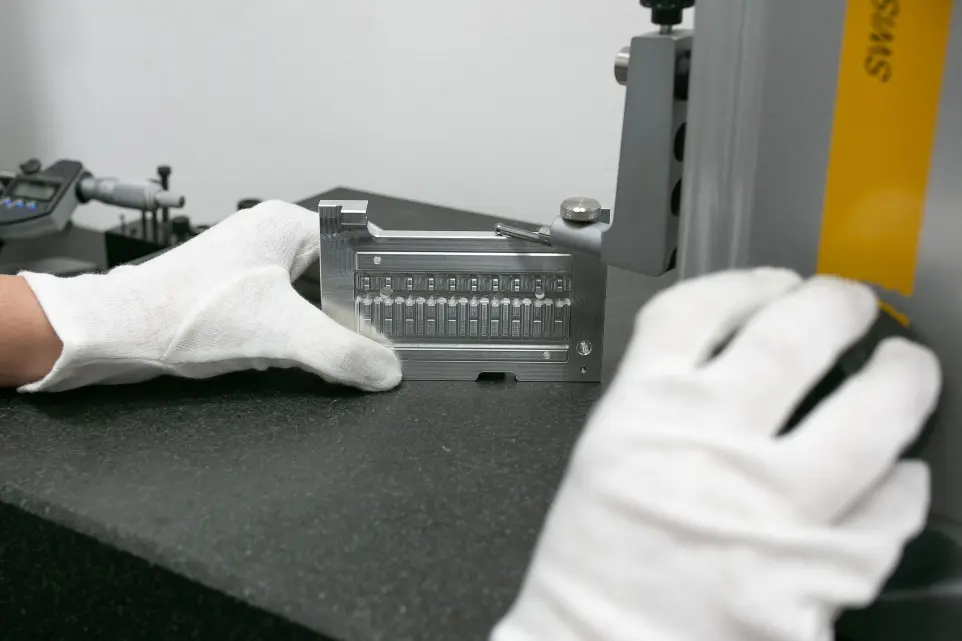
At Sacher, we use a range of advanced measurement methods. These include CMM machines for multidimensional measurements, measuring microscopes, calipers, micrometers, and height gauges. Complementary tools such as profilometers, hardness testers, and gauge blocks are used for calibration and precise verification of material properties.
What measuring instruments do we use?
Our quality control process relies on precise instruments such as:

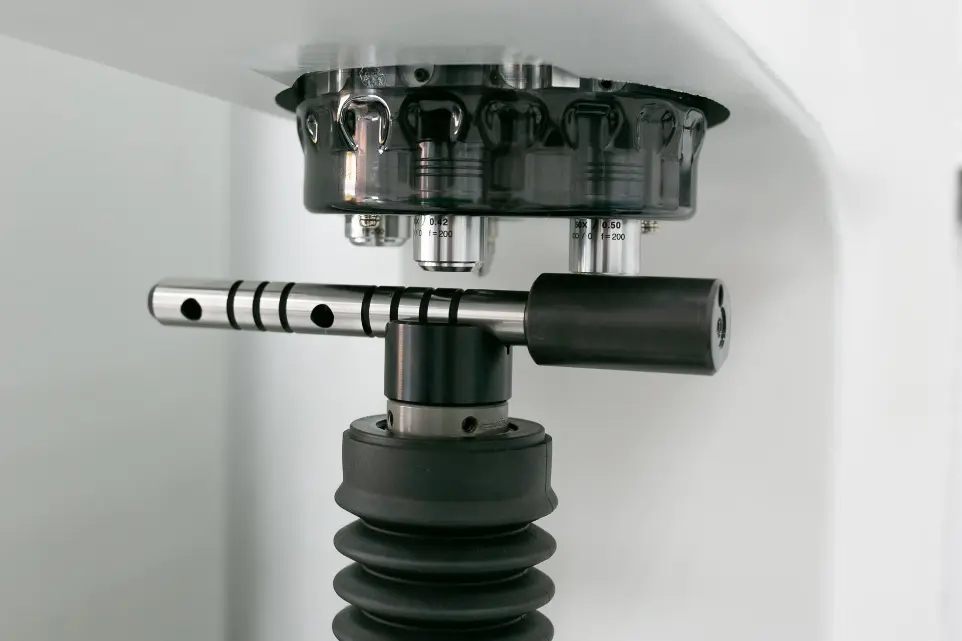
Measuring Microscopes
Enable observation of microscopic details
Hardness Testers
Used to assess the mechanical properties of materials
Profilometers
Analyze the surface of components
Height Gauges, Calipers, and Micrometers
Provide precise dimensional measurements
Gauge Blocks
Ensure accurate calibration of measuring instruments
What certifications confirm our quality standards?
Sacher is ISO 9001 certified, confirming compliance with strict quality management standards. Additionally, the EcoVadis rating reflects our commitment to responsible business practices and sustainable development, which are integral to our quality control procedures.
How do measuring instruments impact production efficiency?
The use of precise instruments such as CMM machines, measuring microscopes, profilometers, calipers, micrometers, hardness testers, height gauges, and gauge blocks enables early detection of potential deviations. This allows for quick corrections, optimization of production processes, and ensures the reliability and repeatability of final products.